Third-party insurance is often cheaper than other types of liability insurance. The National Association of Insurance Commissioners estimates that third-party liability insurance saves consumers an average of $500 per year. These lower rates come from the fact that third-party liability insurance covers less than full liability insurance. That means insurance companies have to pay fewer claims. Here’s how to find out how much 3rd Party Insurance costs in your state. You can also find average third-party insurance prices by state by entering your zip code below.
Cost of auto insurance
The National Association of Insurance Commissioners calculates the average cost of auto insurance when comparing rates. This assumes that all vehicles are covered with liability, collision, and comprehensive coverage. Average insurance costs do not equal the total liability or collision and comprehensive costs of insured vehicles. They represent actual insurance costs and can vary slightly by state. The table below shows the average cost of auto insurance for California drivers. The figure depends on the severity of the accident and whether the other driver was at fault for the accident.
More expensive vehicles generally attract higher insurance premiums than more affordable vehicles. While regular cars are easier on the budget, they are also more susceptible to theft and can increase the cost of comprehensive claims. The make and model of your car also contribute to the average cost of third party insurance. Some car models are safer than others and score better in crash tests. You should consider the cost of repairing or replacing parts on your car and do so when determining your premium.
Once you’ve determined the minimum coverage required by your state, you’ll need to choose a policy that suits your needs. For example, a third-party auto insurance policy will pay for damage to other cars and their property. This coverage will pay for medical expenses for passengers and drivers in an accident. It also covers repairs to damaged vehicles. However, the maximum amount of coverage can vary from policy to policy. So it’s important to choose the best coverage mix for your specific needs.
Third party insurance exclusions
There are various exclusions from third-party liability insurance. The purpose of auto exclusions is to prevent overlap between coverage and liability and to transfer all risk and liability to the auto carrier. Exclusions from liability insurance include the following:
Some exclusions do not apply to all businesses, but some do. These exclude catastrophic risks and widespread exposures. Examples include war, nuclear power, certain pollution claims, and several others. You cannot insure every type of business because these risks are predictable. In those cases, purchase specific coverage. However, it is important to understand all exclusions before purchasing an insurance policy.
Some policies have a severability clause that allows coverage to continue while another policy is active. For example, in Warrilow v. Norrell, the gun discharge exclusion applied to the gun, but not to the injured person. Similarly, in Guaranty Nat’l Ins. Co. v. North River Ins. Co., 909 F.2d 133 (5th Cir. 1995), the employee exclusion was applied separately to the insured.
There are a few other important exclusions from 3rd party liability insurance that are important to understand. First, the employers’ liability exclusion applies to injuries that occur “in the course of employment.” In other words, the employee’s injury must occur during employment and “arise” from employment. This definition can vary from state to state but generally applies to any accident that occurs while the employee is working for the company.
The second exclusion relates to statutory benefits. Statutory benefits are benefits that must be claimed under an employment policy. This type of policy will protect the named insured against work-related injuries. Unfortunately, employers’ liability insurance excludes statutory benefits. Statutory benefits are not typically claimed by injured employees.
Cost of third-party bike insurance
You can also get an Act-only policy. It meets the statutory requirements for third-party damage. Does not cover you for damage to your vehicle. It is cheap and easy to buy. If you get into a major accident, you will have to pay for the damage to the other party. However, this policy is easy to buy with minimal documentation and checks. So, take advantage of it.
If you ride a motorcycle, it is a good idea to buy third-party bike insurance. It covers you for the expenses associated with third-party bike accidents. The premium for third-party bike insurance is determined by the insurer. Regulatory and Development Authority of India and depends on the size and engine capacity of your bike. You are covered for the financial liabilities of other parties in an accident. Not for damage to your bike.
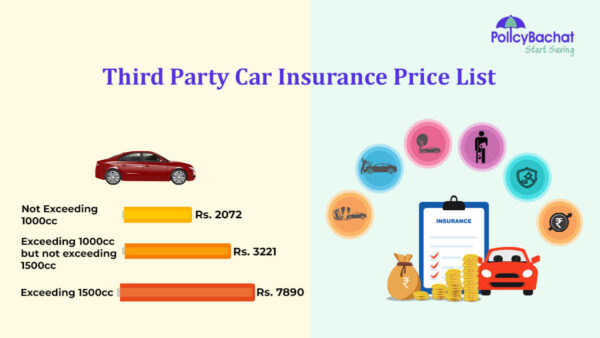
Cost of third-party car insurance in each state
The cost of third-party car insurance varies significantly from state to state. Your home zip code can also affect the price you pay. In general, the more expensive your state is, the higher your premium will be. But many factors can affect the price you pay. These include the number of uninsured drivers, car theft and damage statistics, and the severity of hail and severe weather.
First, the coverage you choose is important. Third-party auto insurance can be a split-limit or single-limit policy. You may see this coverage listed as 25/50/15, but it means the same thing. As long as you have enough coverage, you will be covered if you are in an accident. Depending on your state laws, you may be able to get a lower rate if you pay off your policy early.
The cost of third-party car insurance varies by state. In the United States, a minimum coverage policy costs about $422 per year. This is 46% less than the national average. The cheapest minimum coverage in North Dakota is offered by Geico. Both are highly rated in Delaware, which requires drivers to have PIP insurance. That drives up the price. In Kentucky, drivers pay $1,183 per year for minimum coverage.